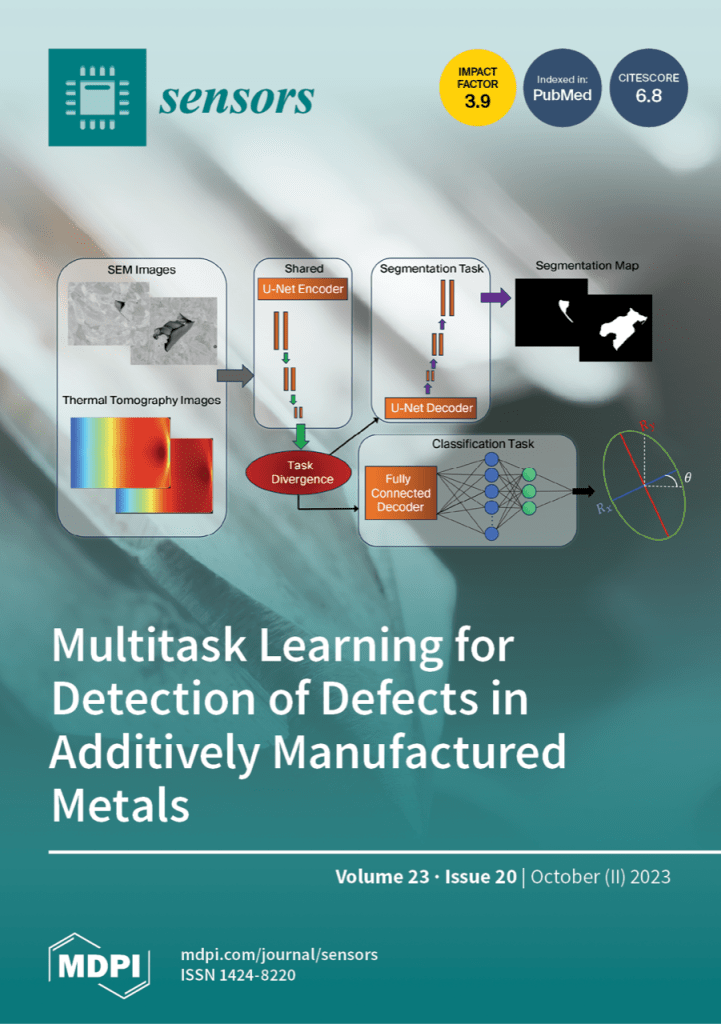
Thermal tomography (TT) is a promising non-contact nondestructive imaging method for the detection of pores in metallic structures printed with the laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) additive manufacturing method. ETI student Sarah Scott from Duke University collaborating with Argonne National Laboratory introduces a novel multi-task learning (MTL) approach, which simultaneously performs a classification of synthetic TT images and segmentation of experimental scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images. Synthetic TT images are obtained from computer simulations of metallic structures with subsurface elliptical-shape defects, while experimental SEM images are obtained from imaging of LPBF-printed stainless-steel coupons. The results of this study show that the MTL network performs better in both the classification and segmentation tasks, as compared to the conventional approach when the individual tasks are performed independently of each other. (view this paper)
